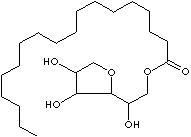
| SORBITAN
STEARATE
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS NO. | 1338-41-6 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EINECS NO. | 215-664-9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FORMULA | C24H46O6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOL WT. | 430.62 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
H.S. CODE |
3402.13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TOXICITY |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES |
Sorbitol, Fatty acid |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
SURFACTANTS / |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SYNONYMS | D-Glucitol, anhydro-, monooctadecanoate; | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Anhydrosorbitol Stearate; Sorbitan, monooctadecanoate; Sorbitan Monostearate; | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHYSICAL STATE | Cream color flake | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT | 56 - 58 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BOLING POINT | > 100 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | soluble in hot water | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOLVENT SOLUBILITY | soluble in mineral oil and ethyl acetae | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| pH | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HLB VALUE |
5 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
NFPA RATINGS |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FLASH POINT | > 400 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Nonionic surfactants are surface active agents which do not dissociate into ions in aqueous solutions, unlike anionic surfactants which have a negative charge and cationic surfactants which have a positive charge in aqueous solution. Nonionic surfactants are more widely used as detergents than ionic surfactants because anionic surfactants are insoluble in many hard water and cationic surfactants are considered to be poor cleaners. In addition to detergency, nonionic surfactants show excellent solvency, low foam properties and chemical stability. It is thought that nonionic surfactants are mild on the skin even at high loadings and long-term exposure. The hydrophilic group of nonionic surfactants is a polymerized alkene oxide (water soluble polyether with 10 to 100 units length typically). They are prepared by polymerization of ethylene oxide, propylene oxide, and butylene oxide in the same molecule. Depending on the ratio and order of oxide addition, together with the number of carbon atoms which vary the chemical and physical properties, nonionic surfactant is used as a wetting agent, a detergent, or an emulsifier. Nonionic surfactants include alcohol ethoxylates, alkylphenol ethoxylates, phenol ethoxylates, amide ethoxylates, glyceride ethoxylates (soya bean oil and caster oil ethoxylates), fatty acid ethoxylates, and fatty amine ethoxylates. Another commercially significant nonionic surfactants are the alkyl glycosides in which the hydrophilic groups are sugars (polysaccharides). The term sorbitan describes the anhydride form of sorbitol, whose fatty acids are lipophilic whereas sorbitol body is hydrophilic. This bifunctionality in one molecule provides the basic properties useful in cleaners, detergents, polymer additives, and textile industry as emulsifiers, wetting agents, and viscosity modifiers. Sorbitan esters are rather lipophilic (or hydrophobic) surfactants exhibiting low HLB (Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance) values; having an affinity for, tending to combine with, or capable of dissolving in lipids (or water-insoluble). While, the ethoxylated sorbitan esters are hydrophilics exhibiting high HLB values; having an affinity for water; readily absorbing or dissolving in water. The type of fatty acid and the mole number of ethylene oxide provides diverse HLB values for proper applications. HLB numbers describe following characterestics: <10 : Lipid soluble (or
water-insoluble) HLB values of sorbitan compounds are:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
Cream color flake | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACID VALUE |
5.0
max
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HYDROXYL VALUE |
230
- 260
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SAP VALUE |
140 - 160 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOISTURE |
1.0%
max
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRANSPORTATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PACKING |
20kgs in bag |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HAZARD CLASS | Not regulated | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UN NO. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF FATTY ACID |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fatty Acids are aliphatic carboxylic acid with varying length hydrocarbon chains at one end of the chain joined to terminal carboxyl (-COOH) group at the other end. The general formula is CnH2n+1COOH or R-(CH2)n-COOH. Fatty acids are predominantly unbranched and those with even numbers of carbon atoms between 12 and 22 carbons long react with glycerol to form lipids (fat-soluble components of living cells) in plants, animals, and microorganisms. Fatty acids all have common names respectively lilk lauric (C12), MyrIstic (C14), palmitic (C16), stearic (C18), oleic (C18, unsaturated), and linoleic (C18, polyunsaturated) acids. The saturated fatty acids have no double bonds, while oleic acid is an unsaturated fatty acid has one double bond (also described as olefinic) and polyunsaturated fatty acids like linolenic acid contain two or more double bonds. Lauric acid (also called Dodecanoic acid) is the main acid in coconut oil (45 - 50 percent) and palm kernel oil (45 - 55 percent). Nutmeg butter is rich in myristic acid (also called Tetradecanoic acid ) which constitutes 60-75 percent of the fatty-acid content. Palmitic acid(also called Hexadecylic acid ) constitutes between 20 and 30 percent of most animal fats and is also an important constituent of most vegetable fats (35 - 45 percent of palm oil). Stearic acid ( also called Octadecanoic Acid) is nature's most common long-chain fatty acids, derived from animal and vegetable fats. It is widely used as a lubricant and as an additive in industrial preparations. It is used in the manufacture of metallic stearates, pharmaceuticals, soaps, cosmetics, and food packaging. It is also used as a softener, accelerator activator and dispersing agent in rubbers. Oleic acid (also called octadecenoic acid) is the most abundant of the unsaturated fatty acids in nature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRICES |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||